Evolving Landscape of SEO Ranking: Understanding Interaction to Next Paint
In March 2024, First Input Delay (FID) will be replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP), a pending Core Web Vital metric. The seamless and engaging user experience has become a paramount goal for developers and designers. Interaction to Next Paint (INP) has emerged as a promising solution for faster loading times and more interactive websites.
Using data from the Event Timing API, INP evaluates responsiveness. A poor user experience occurs when an interaction makes a page unresponsive. INP keeps track of each user’s latency interactions with the website. Then it reports a single value that all interactions came within. A low INP indicates that the page promptly handled most user interactions.
INP focuses on optimizing the rendering process of web pages, ensuring that users can interact with the content as quickly as possible. This article delves into the world of INP, exploring its significance and potential applications in web design and development. We will examine the INP benefits, implementation techniques, best practices, etc, associated with INP.
PermalinkWhat is INP, and How Does It Work?
According to Chrome usage data, 90% of a user’s time on a web page is spent after it loads. It is crucial to test responsiveness at all page lifecycle stages carefully. That’s where the INP metric comes into play.
INP is a metric that measures how responsive a website is overall to user interactions by tracking all click, tap, & keyboard interactions that occur during a user’s visit to a page. The final INP value represents the most prolonged recorded interaction by excluding outliers.
Something about how INP is determined as a collection of event handlers that trigger in response to one logical user motion is an interaction.
For instance, “tap” interactions on a touchscreen device involve several events, including pointer up, down, and click. JavaScript, CSS, built-in browser controls (such as form elements), or any combination can be used to drive interaction.
From when the user starts the interaction until the following frame is presented with visual feedback, an interaction’s latency is the sum of the individual most prolonged durations of a set of event handlers that drives the interaction.
PermalinkINP vs. FID: How is INP Different from First Input Delay (FID)?
INP considers all page interactions, whereas First Input Delay (FID) considers the first interaction. It also accounts for the time it takes to run event handlers and deliver the next frame during the first interaction.Given that FID is also a load responsiveness metric, the idea behind it is that a page creates an excellent first impression if the user has little to no input delay during the first interaction while it is still loading.
INP is about more than just first impressions. INP is a more accurate measure of overall responsiveness than FID since responsiveness can be evaluated thoroughly by sampling all interactions.
PermalinkWhat Is a Good Interaction to Next Paint (INP) Score, and How To Improve It?
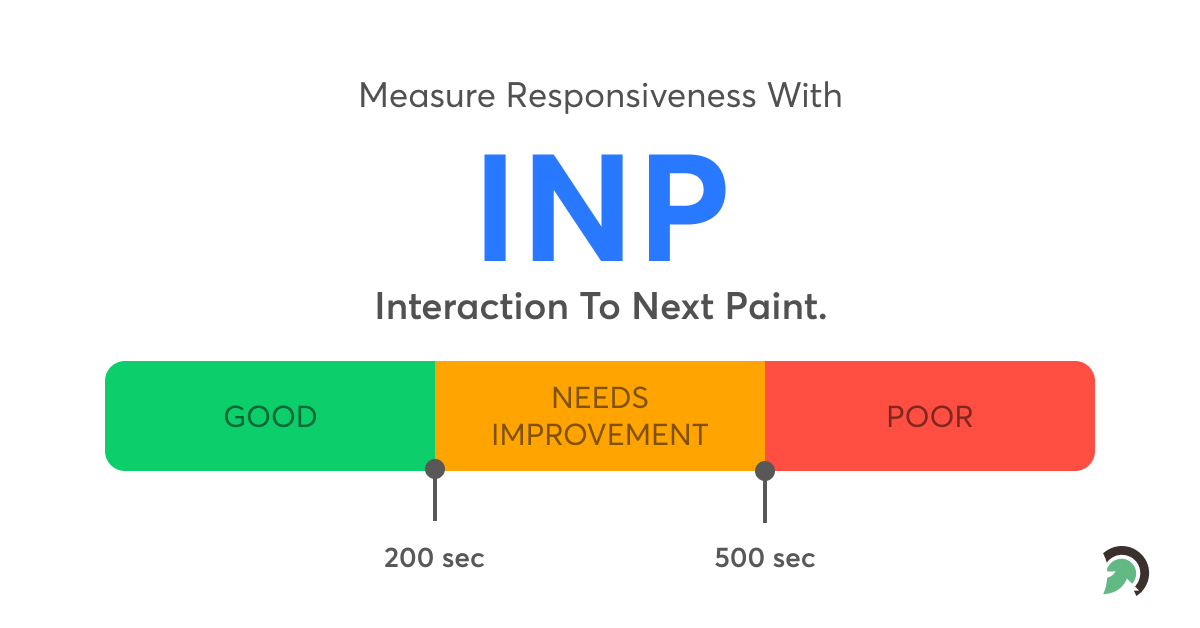
According to Google’s web.dev documentation, a good INP score is 200 milliseconds or below. It reads as follows:
An INP of 200 milliseconds or less indicates that your page is responsive.
An INP between 200 and 500 milliseconds indicates that your page’s responsiveness needs to be improved.
An INP greater than 500 milliseconds indicates that your page’s responsiveness is poor.
Google adds that INP is currently in the experimental stage and that its suggested guidelines for using this metric may change.
The most effective technique to lower INP is to decrease the amount of CPU processing on your page. Additionally, you can run more of your code simultaneously to update the user’s UI immediately while other work is still being done.
To INP website optimization, you must work on below crucial steps –
Permalink1. Improved User Engagement and Interaction
By prioritizing INP in web design and development from web developers, websites can provide users with a more engaging and interactive experience. Users no longer have to sit and wait for a page to load fully before being able to click or interact with elements of the site.
If you improve INP performance, users can engage with the website immediately, leading to increased satisfaction and a higher likelihood of continued interaction.
Permalink2. Enhancing Website Performance and Speed
INP also plays a crucial role in enhancing website performance and speed. When a website has a fast INP, it loads quickly and becomes responsive, keeping users engaged and preventing them from bouncing away.
Additionally, a speedy website creates a positive impression and improves overall user satisfaction, contributing to the website’s success.
Permalink3. Boosting Conversion Rates with INP
Regarding eCommerce websites or any site with conversion goals, INP can be a game-changer.
By reducing the time it takes for a website to become interactive, INP increases the chances of users completing desired actions, such as purchasing or submitting a form. By providing a seamless and responsive experience, INP can significantly boost conversion rates.
PermalinkStep-by-step Guide on Implementing Interaction to Next Paint (INP) on Your Website
Read Here: Guide on Implementing Interaction to Next Paint (INP) on Your Websit
INP is a crucial new metric and Google ranking factor that SEO experts and digital marketers should monitor. Understanding INP and optimizing it can help your website work better, give users a better experience, and rank higher in search results.
It is vital for eCommerce sites, social networking platforms, gaming platforms, and more that rely significantly on user interactions.
But knowing where to begin with performance metrics can be challenging if you’re new to website performance. In this case, you should go with a highly reputed Digital Marketing Agency like EvinceDev. Our experts can help you with an enhanced Interaction to Next Paint (INP) score & give you a competitive edge.
